An internal “body clock” known as circadian rhythm regulates your sleep cycle by controlling when you feel tired or refreshed. In accordance with this rhythm, we get increasingly tired throughout the day.
This sleep drive – also known as sleep-wake homeostasis – may be linked to adenosine, an organic compound produced in the brain that increases throughout the day causing us to feel more and more tired, until the moment it’s broken down during sleep.
Light also influences the circadian rhythm because brain contains a special region that process the signals through the eyes to determine whether it is day or night. Combined with this information either, melatonin, a hormone that induces drowsiness or cortisol, a hormone that promotes energy and alertness gets released.
Stages of Sleep
Once we fall asleep, our bodies follow a sleep cycle divided into four stages. The first three stages are known as non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, and the final stage is known as rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
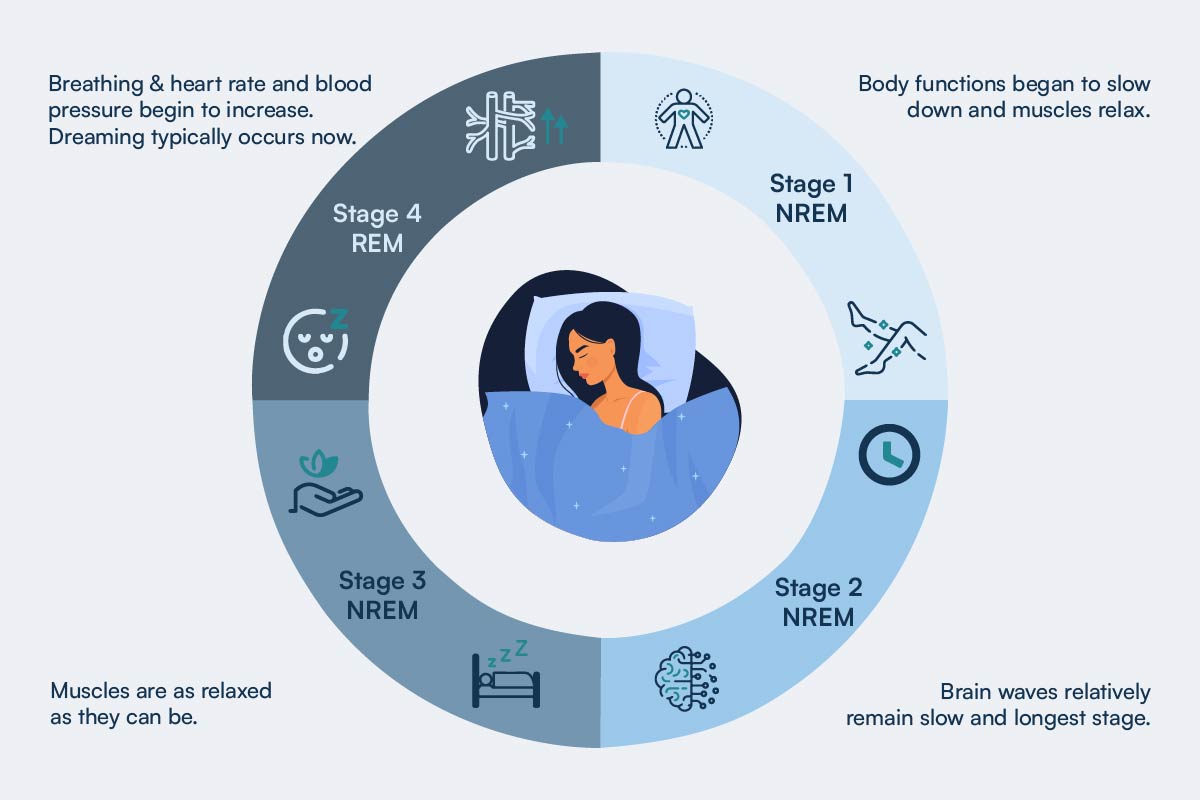
Stage 1 NREM: This first stage marks the transition between wakefulness and sleep, and consists of light sleep. Within several minutes body functions began to slow down and muscles relax.
Stage 2 NREM: During this deeper sleep stage, body continues to slow down and relax. In addition, eye movements cease and body temperature decreases while brain waves relatively remain slow. This is typically the longest stage.
Stage 3 NREM: This stage plays an important role in making you feel refreshed and alert the next day. Heartbeat, breathing, and brain wave activity all reach their lowest levels, and the muscles are as relaxed as they can be.
Stage 4 REM: First REM stage occurs about 90 minutes after falling asleep. Breathing & heart rate, and blood pressure begin to increase. Dreaming typically occurs now. Hence arms and legs become paralyzed, most likely to prevent us from physically acting out on our dreams. Numerous studies link REM sleep to memory consolidation and the process of converting short-term memories into long-term ones.
These four stages repeat cyclically throughout the night until we wake up. For most people, duration of each cycle lasts about 90-120 minutes. NREM sleep constitutes about 75% to 80% of each cycle. We might also wake up briefly during the night but not remember the next day. These episodes are known as “W” stages.
How Much Sleep Do Humans Need?
The right amount of sleep largely depends on your age. The National Sleep Foundation recommends the following daily sleep allotment for different age groups.

But what we need for a good sleep ?

Thank you for your reading...